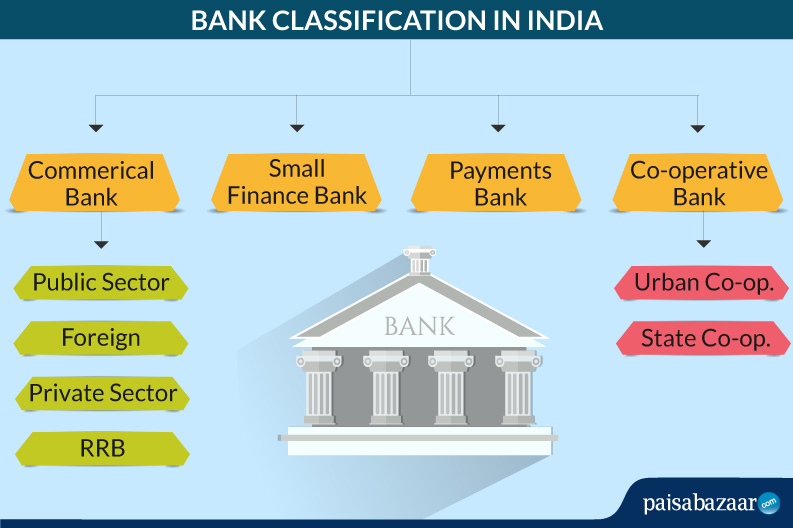
The banking industry handles finances in a country including cash and credit. Banks are the institutional bodies that accept deposits and grant credit to entities and play a major role in maintaining the economic stature of a country. Given their importance in the economy, banks are kept under strict regulation in most countries. In India, the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) is the apex banking institution that regulates the monetary policy in the country.