Note: The information on this page may not be updated. For latest information, click here.
NPS is a type of investment that working individuals may choose to lock in their funds for the purpose of safe retirement. On the other hand, Mutual Funds are open-ended, professionally managed investment options that pool in money from multiple investors to purchase securities. However, both are market-linked investment plans.
National Pension System and Mutual Funds, both allow investors to pool in their funds at fixed, regular intervals (in case you choose to invest via SIP) for the long term. It must be noted that many investors equate SIPs to mutual funds and use them interchangeably. Whereas, SIPs (Systematic Investment Plans) are a way of investing in Mutual Funds (that are an investment option for investors).
It is of importance that you understand both the investment options before making a choice of where and how to invest. Let’s first learn about the National Pension System and Mutual Funds as individual investment options.
Table of Contents :
What is NPS
A social security initiative launched by the central government, National Pension System is a pension plan launched in January 2004 for the financial welfare of the employees working in the government sector. Eventually, by the year 2009, the scheme was made available to all the working professionals. NPS is popular as a retirement scheme and for the tax benefits that come with it.
Also Read: All that you should know about NPS
Features of National Pension System
- As of now, the National Pension System allows employees from the private, public and unorganized sectors to contribute to a pension account regularly until the course of his employment
- 50%-75 % of the investments made in NPS are exposed to equity depending on your risk profile. Given the limit, the equity exposure of the investor’s investment will reduce by 2.5% every year after the investor turns 50 years old. This stabilizes the risk-return equation in the interest of the investor
- Upon retirement, the employees can withdraw a part of their corpus in a lump sum and invest the remaining in annuity in order to secure a regular income even after retirement
- The scheme is open to all employees irrespective of their job profiles, job type or job location. However, the individuals employed in the armed forces cannot avail the benefits of this scheme
- NPS tends to offer returns that are more than the investments made in PPF
- Going by the historical performance of the scheme, it has approximately delivered 8%-10% returns on an average, annually
- You have the option of active choice or passive choice to adjust your risk exposure to asset classes
Advantages of Investing in NPS
- Investments made in NPS involve very low risk, as it is government backed
- NPS is considered to be one of the safest investment options
- NPS meets the long-term investment needs of investors
- The scheme offers tax benefits under Section 80C and Section 80CCD of the Income Tax Act
- NPS is considered to be the only investment option that allows you to change your fund manager once in a financial year from the 7 funds available
- Investors of NPS, allocate their funds to four asset classes namely- Equity, Corporate Debts, Government Bonds and Annuity. Since NPS investments are exposed to various instruments, the risk is scattered, thereby reducing the risk of equity market volatility
What are Mutual Funds
Mutual Funds can be referred to as a basket of multiple and varied financial instruments that generate returns over a long period of time. Experienced professionals, called fund managers, are appointed by AMCs to carefully administer the funds of investors and change allocations according to the fluctuations in the market.
Learn more about Mutual Funds here.
Types of Mutual Funds
Based on the allocation of their assets, Mutual funds can majorly be classified into the following 3 categories-
- Equity Mutual Funds- More than 70% of the assets are invested in equity stocks of companies. Equity mutual funds are considered to offer high returns and growth options in the long term.
- Debt Mutual Funds- Majority of the assets in these funds are allocated to fixed-income securities of companies such as government securities. Debt mutual funds are known to involve lesser risk and have a fixed maturity date.
- Hybrid Mutual Funds- These funds are known to invest in a mix of equity and debt securities of funds. Hybrid mutual funds tend to benefit from the features of both, offering high returns from equity investment with low risk from debt investments.
Modes of Investing in Mutual Funds
It must be noted that while investing in mutual funds, investors have a choice of investing via SIPs or Lump sum, depending on their own ease.
- SIP or Systematic Investment Plan is a facility offered by the fund houses wherein you can invest your corpus in mutual funds at pre-defined, fixed intervals. This keeps investors away from the burden of pooling in all their financial savings all at once.
- On the other hand, using the lump sum mode of investing, investors must pool in the corpus in one go. Lump sum investments in mutual funds do not allow investors to make changes to their invested amount during the tenure of investment
Suggested Read: Lump sum vs SIP mode of investing in mutual funds
Features of Mutual Funds (SIP)
- One can start investing in Mutual Funds (via SIPs) with an amount as low as Rs.500
- Investors can choose to invest in Mutual Funds at pre-defined intervals on weekly/monthly/quarterly or yearly basis, so that there is no burden of pooling in huge sums in one go
- SIP installments in mutual funds are to be paid at fixed intervals, which develops a sense of responsibility and reliability among the investors
- Depending upon their income, investors can also flexibly choose to increase or withdraw their invested principal amount
- For instance, the feature of top-up in SIPs allows investors to increase their SIP amount by a fixed amount at pre-defined intervals, whilst also increasing their gains
As you decide which mutual fund to invest in, You must also go through the returns delivered by any fund in the past. Additionally, it is advised that you have a fair idea of how much returns to expect in a given time period. To do so, you can use the Mutual Fund Calculator before making the choice.
Advantages of Mutual Funds
- Investors with investment objectives for the long term can benefit from their investments in mutual funds due to the concept of rupee cost averaging (in SIP investments)
- Power of Compounding is another feature that helps investors gain from their investments in Mutual Funds. This ensures that investors benefit not only from the principal amount invested but also from the gains on principal amount
- In comparison to the interest earned on conventional modes of investing, FDs, for instance, Mutual Funds deliver higher returns that help to beat inflation in an efficient manner
- Mutual Funds are considered to be a flexible mode of investment as they allow investors to add or withdraw their corpus at ease
- Certain mutual funds also offer tax benefits to investors. For example, investments in ELSS (Equity Linked Savings Scheme) offer tax exemption on investments up to Rs.1.5 Lakh under Section 80C of the Income Tax Act
Read More: List of Top Ranked Mutual Funds
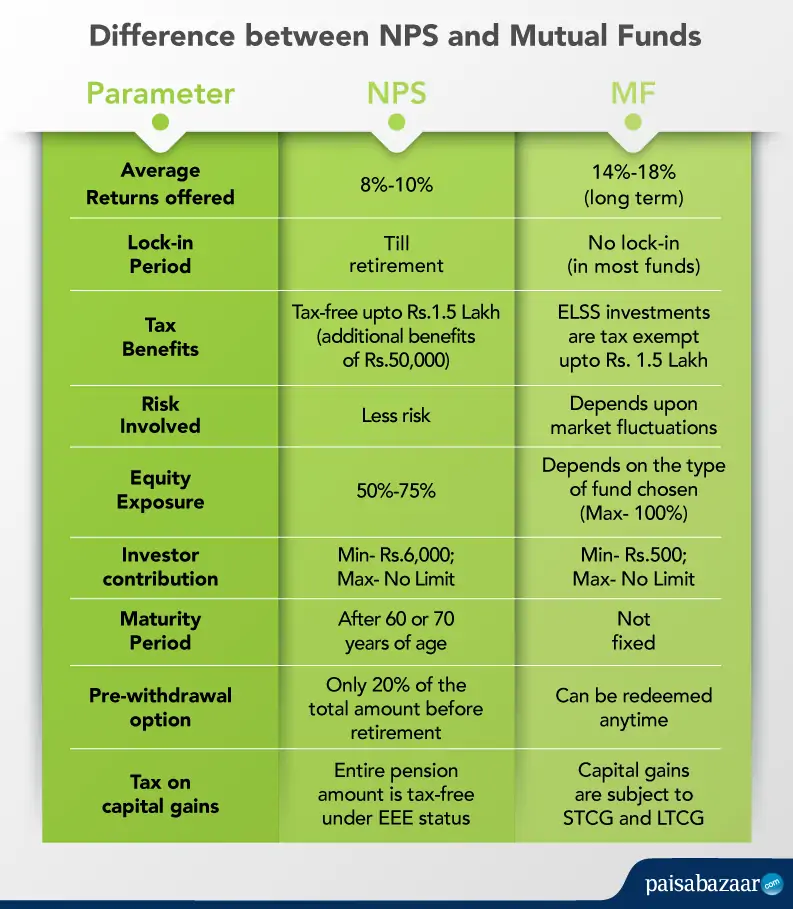
NPS or Mutual Funds- Which is Better
When it comes to choosing between the given investment options, both NPS and Mutual Funds instill a sense of financial discipline in your life as the amount gets debited from your registered account at pre-defined intervals automatically (especially if invested via the SIP mode).
Mutual Funds, in most cases, also act as emergency funds because of the level of flexibility offered by them. You can choose to withdraw your funds (with no or some exit load based on the scheme). Hence, it is advised to invest in NPS when retirement, along with tax benefits is your goal, and you have a less risk appetite.
Additionally, you can also save on taxes during the period of your employment as NPS offers a tax deduction of upto Rs.1.5 Lakh for your and your employer’s contribution to the scheme, under Section 80CD of the Income Tax Act. Moreover, you can also claim any additional self contribution (up to Rs.50,000) to the scheme under Section 80CCD as NPS tax benefit.
Along with this, NPS was put into the EEE (Exempt-Exempt-Exempt) category in the 2019 budget. This implies that NPS subscribers can claim tax deductions on NPS contributions, returns earned on the NPS contributions are also tax exempt and with tax benefits extended on lump sum withdrawal, NPS now qualifies to be an Exempt-Exempt-Exempt (EEE) category product. On the other hand, capital gains in Mutual funds are subject to short term and long term taxation.
Given their similarities and differences, you should make a wise choice between both the investment options depending upon your financial objectives. If the main motive behind investing is to secure your retirement financially, NPS should be your choice. Mutual Funds are generally popular for individuals who have a high risk appetite, may have short-term financial goals and can also serve other goals.
Investing in NPS via SIP
Mutual fund investments via SIP allow investors to register an auto-debit mandate with their banks. This allows them to stay away from the hassle of paying their SIP amount every week/month/quarter/year as the process gets done automatically.
However, if you decide to invest in NPS, you can still choose to invest via the SIP mode either manually or using the auto-debit option. You can use the manual option to pay your SIP installment if your bank does not offer an auto-debit feature through the online portal.
On the other hand, you can opt for the auto-debit feature by notifying your bank about your NPS investment in NPS. Additionally, investors in the NPS Corporate Model and the Government Model have a fixed amount deducted from their salaries every month and get it invested in NPS, which automatically acts as an SIP.
Important Notice: NPS Service Discontinuation on Paisabazaar. Read more

