Salary is a fixed amount of money paid to an employee by the employer (Government, Multi-National organisations, Public Sector Departments as well as many other private sector companies) in return for the work performed. Salary is generally paid in fixed intervals, for example, monthly payments at the end of the month of one-twelfth of the annual salary.
The salary paid to the employees comprises a number of components such as basic salary, allowance, perquisite, etc. Knowledge of these components is important since it helps keep the employee informed about what is being saved and on what they can claim the tax exemption. On this page, we will explain everything related to salary, its calculation and its components.

Get Free Credit Report with monthly updates. Check Now
Salary Structure in India
Structuring salaries is a prescribed task for every HR and Payroll professional. Salary structure includes the details of the salary being offered, in terms of the breakup of different components constituting the compensation. Any particular change in the salary structure can have a major impact on what the employee does, such as the kind of tax exemptions claimed.
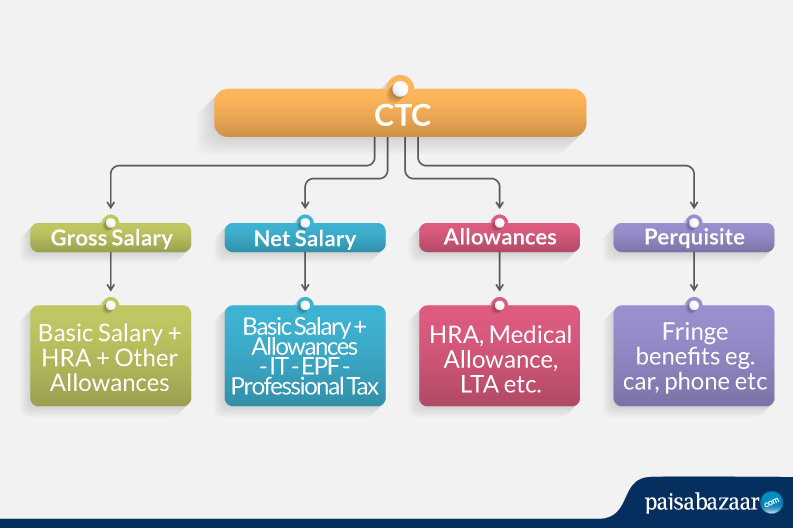
The process of Payroll calculation can be hectic if not streamlined. In India, however, while the payroll processing differs from one company to another, the salary elements remain the same. Terms like CTC, Net Pay, Gross Salary, Allowances, Perquisites, Deductions, Bonus, Incentives etc. are all essential components of the salary structure.
Components of Salary Structure
Suggested Read: New at Job? Know everything about your Salary Slip
Find Credit Cards on the Basis of your Salary
Select the Pre-approved Credit Card from the List and Apply Instantly
How to Calculate your Take-Home Salary?
In order to calculate your Take-Home Salary or Net Salary, follow these steps:
Step 1- Calculate Gross Salary
Gross Salary= Basic Salary + HRA + Other Allowances
Alternatively,
Gross Salary= CTC – (EPF + Gratuity)
Step 2- Calculate Taxable Income
Taxable Income = Income (Gross Salary + other income) – Deductions
In order to calculate the part of income which is taxable, you need to subtract allowances (LTA, Conveyance Allowance, HRA), professional tax, medical bills, medical insurance, tax saving investments, if any and other deductions from your gross salary. Make sure to calculate income from all sources such as house property, capital gains, income from business etc.
Deductions are generally divided into the following sections-
| Section | Nature | Limit |
| 80 C | Basic deductions from total income | Rs. 1.5 lakh |
| 80 TTA | Interest from deposits | Rs. 10,000 on interest, available to an individual and HUF, deduction allowed on interest earned from a savings account with a bank |
| 80 G | Donations to charity | 50% of the donation made is allowed to be deducted from the taxable income |
| 80 E | Education loan | No limit |
| 80 EE | Home loan interest | Maximum Rs 50,000 per financial year |
| 80 D | Medical insurance premium | For self and family- Rs 25,000, For self and family and parents- Rs. 55,000,
For self and family and senior citizen parents- Rs. 80,000 |
Step 3- Calculate Income Tax
Once you calculate the taxable income, you can easily calculate income-tax by referring to the income-tax slab and rates according to the present date. Income tax slabs are revised every year during the budget keeping in mind the individual taxpayers.
As per the revised tax regime, tax slab for individuals below 60 years of age is as follows:
| Income Tax Slab | Tax Rate |
| Up to Rs. 2.5 lakh | Nil |
| Rs. 2.5 lakh to Rs. 5 lakh | 5% (Rs 12,500 tax rebate per section 87A) |
| Rs. 5 lakh to Rs. 7.5 lakh | 10% |
| Rs. 7.5 lakh to Rs. 10 lakh | 15% |
| Rs. 10 lakh to Rs. 12.5 lakh | 20% |
| Rs. 12.5 lakh to Rs. 15 lakh | 25% |
| Rs. 15 lakh and above | 30% |
Step 4- Calculating take-home salary
Your take-home salary will be-
Take Home Salary = Basic Salary + Actual HRA + Special Allowance – Income Tax – Employer’s PF Contribution(EPF)
Let’s understand this with the help of an example:
For example, your CTC is Rs. 8 lakh. The employer gives you a bonus of Rs. 50,000 for the financial year. Your total gross salary will be Rs. 7.5 lakh (Rs. 8 lakh – Rs. 50,000).
You then deduct the professional tax of Rs. 2,400 a year (This is the professional tax in Delhi for the present financial year).
You then deduct the EPF contribution or maximum salary limit of Rs. 15,000 per month, which is 12% of Rs. 15,000 i.e Rs. 1,800 a month or Rs. 21,600 a year. Now you have Rs. 21,600 as yearly contribution made by the employee towards EPF and a similar contribution of Rs. 21,600 made by the employer.
You also have Rs. 3,000 deducted as employee insurance.
Your total deductions will be-
| Total deductions= Rs 2,400 + Rs 21,600 + Rs 21,600 + Rs 3,000 = Rs 48,600. |
Hence, your take-home salary will be:
TAKE HOME SALARY= GROSS PAY – TOTAL DEDUCTIONS= RS. 7,50,000 – RS. 48,600
| RS. 7,01,400 |
Objectives of Perfect Salary Structure
There are mainly three things to be kept in mind while creating the perfect salary structure:
- Should be tax efficient- It should give the employee the opportunity to save as much tax as possible. The salary amount should be divided into components in a way that it should give the employee the opportunity to avail as much tax deduction as possible
- Should reduce the employer’s liability- The salary structure should ideally reduce the liability of the employer. The employer’s contribution to PF, Gratuity etc. should be kept as low as possible
- Should be compliant- Compliance norms like minimum wages and PF laws should be kept in mind while drafting the salary structure

Get Free Credit Report with monthly updates. Check Now
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What is the house rent allowance?
A house rent allowance is a component of the salary that is paid to employees by their employers for meeting the cost of renting a home.
What are the tax benefits that can be claimed on HRA?
The whole of HRA received by employees is not always fully tax-exempt. The actual tax exemption that can be claimed will be the least of the following three:
- The amount received as HRA from the employer
- Actual rent paid minus 10% of salary
- 50% of basic salary for those living in metro cities and 40% for those living in non-metro cities
What is gratuity?
Gratuity is a lump sum benefit paid by employers to those employees who are retiring from the organization. This is only payable to those who have completed 5 or more years with the company. The gratuity amount is paid in gratitude for the services rendered by the individual during the period of employment. According to the Payment of Gratuity Act, 1972, gratuity is calculated as 4.81% of the basic pay. Most firms with a workforce of 10 or more employees come under the Act.
What is the difference between Financial Year and Assessment Year?
A financial year is a year as reckoned for taxing and accounting purposes. It commences from April 1 of a year and ends on March 31 of the following year. Assessment year, on the other hand, is the year in which you file your returns. It is the year in which the income that you have earned in the financial year will be evaluated.
How do you calculate your monthly take home salary? Also How much is the Basic Salary of CTC?
You can calculate Take Home Salary by deducting various provisions from CTC such as employee’s contribution to EPF, Gratuity, Labor welfare fund, etc. Generally, basic salary comprises 40-45% of the CTC.
What is the difference between CTC and Take Home Salary?
CTC means ‘Cost To Company’, it is the total expense incurred by the organization in terms of your compensation for the employment. Take-home salary, on the other hand, refers to the actual payment received by an employee in its bank account as a monthly salary.
How is LTA CTC break up calculated?
Leave Travel Allowance is paid to cover travel expenses incurred by employees within the country. LTA is 8.33% of Basic, it can be fixed depending upon grade and native place of an employee by company.
Is PF calculated on gross salary? What is the percentage of basic salary in gross salary?
In most cases, for those working in the private sector, it’s the basic salary on which the contribution is computed. For instance, if your basic monthly salary is Rs. 30,000, then contribution by you and your employer would be Rs. 3,600 each (12% of basic). The percentage of Basic is either 50% or 60% of the Gross salary.
Latest News on Salary
Dearness Allowance Increased to 34% for Central Government Employees & Pensioners
30-03-2022- As per a recent update, Dearness Allowance (DA) has been increased from 31% to 34% for central government employees and pensioners, effective January 1, 2022. This 3% increase over the existing rate of 31% of the basic pay/pension has been made to compensate of the increase in prices/inflation.