Any individual or HUF can get a tax deduction up to Rs. 1.5 lakh per financial year under Section 80C of the Income Tax Act and its allied sections such as 80CCC and 80CCD. This deduction is not available to partnerships, companies and other corporate bodies. You have to claim this deduction under Section 80C in your income tax return (ITR) which has to be filed by 31st July each year for individuals.
Table of Contents :
 The amount you claim under this section is reduced from your gross total income for the purposes of computing income tax. For example, if your gross total income is Rs. 10 lakh and you have claimed a deduction of Rs. 1.5 lakh under Section 80C, your taxable income becomes Rs. 8.5 lakh.
The amount you claim under this section is reduced from your gross total income for the purposes of computing income tax. For example, if your gross total income is Rs. 10 lakh and you have claimed a deduction of Rs. 1.5 lakh under Section 80C, your taxable income becomes Rs. 8.5 lakh.
Deduction under Section 80C, 80CCC and 80CCD
The deduction under this category is available under Sections 80C, 80CCC and 80CCD. Section 80C includes mutual funds, insurance premium tax saver FDs, PPF and several other schemes. 80CCC governs contributions to specific policies which pay a pension or annuity. 80CCD covers contributions to India’s National Pension System (NPS)
Section 80C Limits
The maximum limit for tax saving under Section 80C is Rs. 1.5 lakh. There is no minimum limit.
Section 80C Schemes
- Investment Schemes: ELSS Mutual Funds, Unit Linked Insurance Policies (ULIPs)
- Insurance Schemes: Term Insurance, Endowment Insurance
- Retirement Savings Schemes: Public Provident Fund (PPF), Employees Provident Fund, National Pension System (NPS)
- Fixed Income Schemes: National Savings Certificate (NSC), Senior Citizens Saving Scheme (SCSS), Sukanya Samriddhi Yojana
- Miscellaneous: Home loan repayment, tuition fee payment

Get FREE Credit Report from Multiple Credit Bureaus Check Now
Eligibility
An individual or HUF can claim a Section 80C deduction. Companies, Limited Liability Partnerships and other bodies cannot claim this deduction under Section 80C.
The following deductions are available under this section:
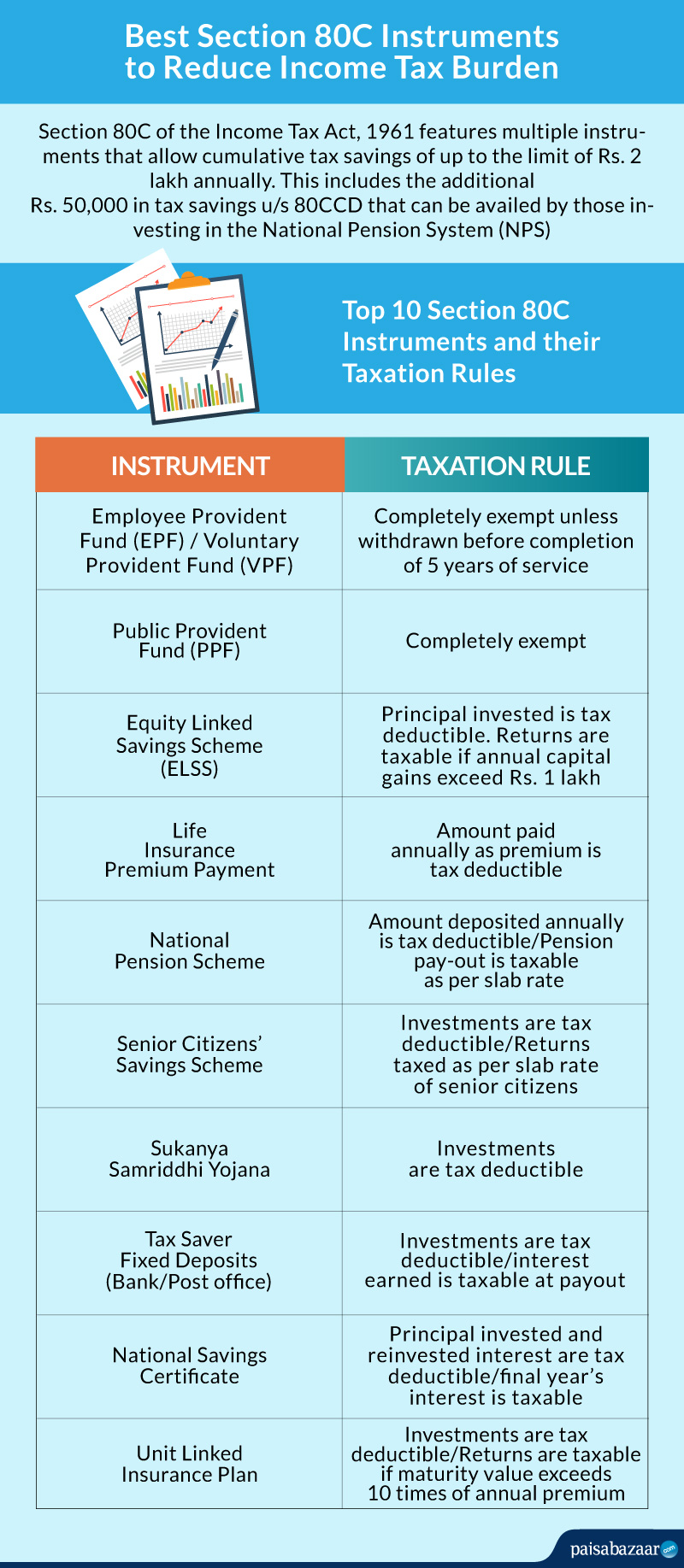
1) Life Insurance Premiums either for yourself or family members. However the insurance policy cannot be terminated within two years of commencement if it is a single premium policy. If it is a multiple premium policy, you must pay at least two years’ premiums. Failure to do so will lead to reversal of Section 80C deduction. Unit Linked Life Insurance Policies (ULIPs) are also eligible for deduction under Section 80C.
Tax on Returns: The returns on life insurance policies, where the insurance cover is at least 10 times the annual premium, are exempt from tax under Section 10(10)(D) of the Income Tax Act.
2) Investment in ELSS mutual funds. ELSS mutual funds have a lock-in of 3 years and invest 80% of their corpus in equities (stocks).
Tax on Returns: ELSS returns above Rs. 1 lakh are subject to long term capital gains tax at a rate of 10%.
3) Public Provident Fund (PPF): This is a government savings scheme with a government-administered interest rate. You can invest in it through most banks and post offices. It has a tenure of 15 years.
Tax on Returns: PPF returns are exempt from tax. However, you have to declare PPF returns in your income tax return each year.
4) Employees’ Provident Fund (EPF): Employees’ contribution to the EPF account is eligible for deduction under Section 80C. Employer’s contribution is also tax free but it is not eligible for deduction under Section 80C.
Tax on Returns: EPF interest rate is tax-free. However, it becomes taxable when you leave service at an EPF registered company. The interest also becomes taxable if EPF is withdrawn before completion of 5 years of service with an EPF-registered company.
5) Tax Saving Fixed Deposit: The 5 year tax-saver fixed deposits at banks and post offices are eligible for tax deduction.
Tax on Returns: The interest on such fixed deposits is fully taxable.
6) National Pension System (NPS): The NPS deduction is granted by Section 80CCD (1) and (2).Employer’s and employees’ contributions to the NPS are both tax deductible under Section 80C. However employer’s contributions cannot be more than 10% of your basic salary + dearness allowance, in order to get the benefit of this section. Self-employed person can also claim this benefit for contributions up to 20% of gross income. In addition, voluntary contributions to the NPS up to Rs. 50,000 are exempted over and above Rs. 1.5 lakh under Section 80 C. These voluntary contributions are covered under Section 80CCD (1B).
Tax on Returns: NPS returns are tax-exempt until maturity. At maturity, 40% of the accumulated corpus is tax free.
Read more on NPS – National Pension System Eligibility, Types, Contribution & Charges
7) National Savings Certificate: National Savings Certificates are a government-backed savings instrument with a 5 year tenure. The interest on these certificates is also eligible for tax deduction under Section 80C.
Tax on Returns: Returns on NSCs are also eligible for tax deduction under Section 80C
8) Senior Citizens’ Savings Scheme (SCSS): This is a government-guaranteed savings instrument with a tenure of 5 years which can be extended for an additional 3 years.
Tax on Returns: SCSS returns are fully taxable at your slab rate
9) Sukanya Samriddhi Yojana: This is a government supported savings scheme for the girl child. It can be opened by parents of a girl child who is below the age of 10. The scheme has a tenure of 21 years or until the girl child gets married after the age of 18.
Tax on Returns: Returns on the Sukanya Samriddhi Scheme are tax free.
10) Tuition fees for any school, college or university for up to two children.
11) Home loan repayment
12) Stamp duty/fee for the transfer of house property to yourself
13) Investment in a tax-saver 5 year fixed deposit
Section 80C Investment Options
| S no | Options | Interest | Lock-in Period | Guaranteed Returns | Risk Profile |
| 1 | ELSS funds | 12-15% (estimated) | 3 years | No | High |
| 2 | PPF | 7.1% | 15 years | Yes | Low |
| 3 | NPS | 8-10% (estimated) | Till retirement | No | High |
| 4 | NSC | 7.7% | 5 years | Yes | Low |
| 5 | FD | 5.75-9.6% (estimated) | 5 years | Yes | Low |
| 6 | ULIP | 8-10% (estimated) | 5 years | No | Moderate |
| 7 | Sukanya Samriddhi | 8.2% | 21 years | Yes | Low |
| 8 | SCSS | 8.2% | 5 years | Yes | Low |
Note: The rates of PPF, NSC, SCSS and Sukanya Samriddhi Yojana are updated as of Q1 FY 2025-26 and are subject to periodic change.

Get FREE Credit Report from Multiple Credit Bureaus Check Now
FAQs on Section 80C of the Income Tax Act
Q. Can both resident Indians and NRIs claim deduction under Section 80C?
Yes, both resident Indians and NRIs are eligible for tax deduction under this section.
Q. What is the difference between a tax deduction and tax exemption?
A tax exemption (such as interest on a tax-free bond) cannot be deducted from your gross total income. For example, if you have a gross total income of Rs. 10 lakh and also get interest on tax-free bonds of Rs. 1 lakh per annum, the additional Rs. 1 lakh will not be taxable. However, this amount will not be reduced from your gross total income of Rs. 10 lakh. On the other hand, a tax deduction will be deducted from your gross total income. For example, if your gross total income is Rs. 7 lakh and you have invested Rs. 1.5 lakh in a tax-saving instrument under Section 80C, your taxable income will become Rs. 5.5 lakh.
Q. Is personal accident insurance covered under Section 80c?
Yes, all types of life insurance premiums are covered. This includes personal accident insurance which pays out in case of death due to an accident. However, the insurance cover must be at least 10 times the annual premium.
Q. Is Section 80C applicable in new tax regime?
No, Section 80C deductions are not available under the new tax regime.
